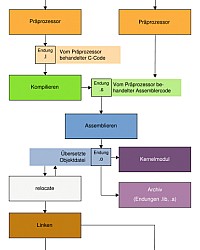
Javac
Native und nicht-native Programmiersprachen
Nicht-native Programmiersprachen
HTML/CSS: keine Programmiersprache sondern Beschreibungssprache!
Javascript: Programmiersprache im Web im Kontext von z.B. jquery.js oder node.js
Shell (TCSH) Beispiel Quelltext (Hello.sh):
Ben├Âtigte Software: sudo apt install tcsh imagemagick
#
# to run the example, type the following on the terminal:
# > ./Hello.sh
foreach image (*.jpg)
convert $image $image:r.png
end
Bottom Line: Programmausf├╝hrung mit Argumenten, Variablen sind Zeichenketten → Scripting
Python Beispiel Quelltext (Hello.py):
Ben├Âtigte Software: python3 -V
#
# to run the example, type the following on the terminal:
# python3 Hello.py
from datetime import datetime
now = datetime.now()
current_time = now.strftime("%H:%M:%S")
print("Hello, Python!")
print("Current Time =", current_time)
Bottom Line: Variablen nicht streng typisiert, Einr├╝ckung ersetzt {} → Scripting
Java Beispiel Quelltext (Hello.java):
Ben├Âtigte Software: sudo apt install default-jdk
//
// to compile and run the example, type the following on the terminal:
// > javac Hello.java
// > java Hello
//
// output:
// > fibo(10) = 55
public class Hello
{
protected static int fibo(int n) {
if (n <= 0)
return(0);
else if (n <= 2)
return(1);
else
return( fibo(n-1) + fibo(n-2) );
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 10;
System.out.println("fibo(" + n + ") = " + fibo(n) );
}
}
Bottom Line: Variablen streng typisiert, Objektorientierung, Anweisungssyntax weitestgehend an C orientiert, Zwischencode
Native Programmiersprachen
C Beispiel Quelltext (Hello.c):
Ben├Âtigte Software: sudo apt install gcc
to compile and run the example, type the following on the terminal:
> gcc Hello.c -o Hello
> ./Hello
output:
> fibo(10) = 55 */
#include <stdio.h>
unsigned int fibo(unsigned int n)
{
if (n <= 0)
return(0);
else if (n <= 2)
return(1);
else
return( fibo(n-1) + fibo(n-2) );
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int n = 10;
printf("fibo(%d) = %d\n", n, fibo(n));
return(0);
}
Bottom Line: Variablen streng typisiert, keine Objektorientierung → C++
Pascal Beispiel Quelltext (Hello.pas):
Ben├Âtigte Software: sudo apt install fp-compiler
uses crt;
(* to compile and run the example, type the following on the terminal:
> fpc Hello.pas
> ./Hello *)
function fibo(n: integer): integer;
begin
if (n <= 0) then
fibo := 0
else if (n <= 2) then
fibo := 1
else
fibo := fibo(n-1) + fibo(n-2);
end;
var n : integer = 10;
begin
write('fibo(');
write(n);
write(') = ');
writeln(fibo(n));
end.
Bottom Line: Variablen streng typisiert, keine Objektorientierung, Syntax nicht an C orientiert
Weitere: C++, Rust, Go, Ada, Fortran, …
Auflistung der vorgestellten Kommandozeilen-Programme:
- kate & emacs
- tcsh & bash
- python3
- javac & java
- gcc
- fpc
- more & less