Computergrafik
GL Tesselierungsbeispiel
← GL Tesselierung | ● | GL PolygonMode →
Tesselierung der Funktion
$f(x,y)=sin(\sqrt{x^2+y^2})$
durch regelmäßiges Gitter aus Quads (Quadmesh):
double func(double x,double y)
{return(3*sin(sqrt(x*x+y*y)/3));}
glBegin(GL_QUADS);
for (i=-100; i<=100-step; i+=step)
for (j=-100; j<=100-step; j+=step)
{
float f0=func(i,j);
glColor3f(0,f0,f0);
glVertex3d(i,j,f0);
float f1=func(i+step,j);
glColor3f(0,f1,f1);
glVertex3d(i+step,j,f1);
float f2=func(i+step,j+step);
glColor3f(0,f2,f2);
glVertex3d(i+step,j+step,f2);
float f3=func(i,j+step);
glColor3f(0,f3,f3);
glVertex3d(i,j+step,f3);
}
glEnd();
{return(3*sin(sqrt(x*x+y*y)/3));}
glBegin(GL_QUADS);
for (i=-100; i<=100-step; i+=step)
for (j=-100; j<=100-step; j+=step)
{
float f0=func(i,j);
glColor3f(0,f0,f0);
glVertex3d(i,j,f0);
float f1=func(i+step,j);
glColor3f(0,f1,f1);
glVertex3d(i+step,j,f1);
float f2=func(i+step,j+step);
glColor3f(0,f2,f2);
glVertex3d(i+step,j+step,f2);
float f3=func(i,j+step);
glColor3f(0,f3,f3);
glVertex3d(i,j+step,f3);
}
glEnd();
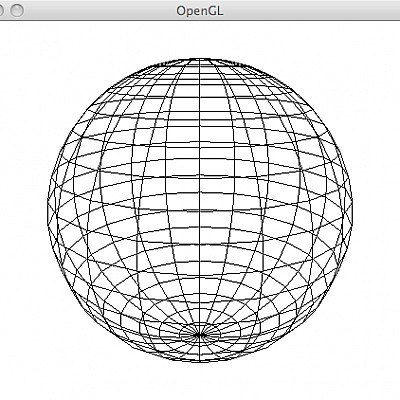
Tesselierung einer Kugel in Polarkoordinaten:
Kugelkoordinaten:
$ f(\alpha,\beta) = \left( \begin{array}{c} sin(\alpha)sin(\beta) \\ cos(\beta) \\ cos(\alpha)sin(\beta) \end{array} \right), \alpha\in[0,2\Pi], \beta\in[0,\Pi] $
for (j=0; j<=200-step; j+=step)
{
glBegin(GL_QUAD_STRIP);
for (i=0; i<=200; i+=step)
{
alpha=(float)i/100*M_PI;
beta1=(float)j/100*M_PI/2;
beta2=(float)(j+step)/100*M_PI/2;
glVertex3d(sin(alpha)*sin(beta1),
cos(beta1),
cos(alpha)*sin(beta1));
glVertex3d(sin(alpha)*sin(beta2),
cos(beta2),
cos(alpha)*sin(beta2));
}
glEnd();
}
{
glBegin(GL_QUAD_STRIP);
for (i=0; i<=200; i+=step)
{
alpha=(float)i/100*M_PI;
beta1=(float)j/100*M_PI/2;
beta2=(float)(j+step)/100*M_PI/2;
glVertex3d(sin(alpha)*sin(beta1),
cos(beta1),
cos(alpha)*sin(beta1));
glVertex3d(sin(alpha)*sin(beta2),
cos(beta2),
cos(alpha)*sin(beta2));
}
glEnd();
}
← GL Tesselierung | ● | GL PolygonMode →