Computergrafik
Bresenham
← Baryzentrische Koordinaten Rechenbeispiel | ● | GL Antialiasing →
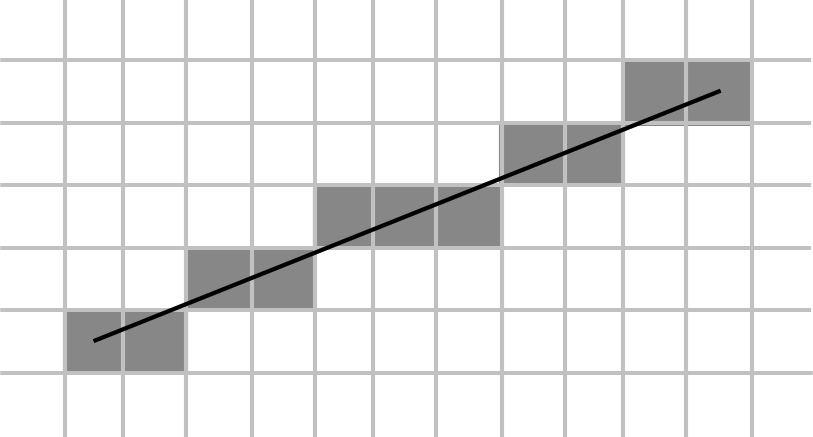
Wie werden Linien gezeichnet? Die Rasterisierung einer Linie:

Naiver Rasterisierungsalgorithmus f├╝r eine Linie:
// Naive algorithm
// int xstart, ystart = start point of line segment
// int xend, yend = end point of line segment
// double dx = xend - xstart;
// double dy = yend - ystart;
double slope = dy/dx;
double x = xstart;
double y = ystart;
for (int t=0; t<dx; t++)
{
setPixel(x,y);
x++;
y+=slope;
}
// int xstart, ystart = start point of line segment
// int xend, yend = end point of line segment
// double dx = xend - xstart;
// double dy = yend - ystart;
double slope = dy/dx;
double x = xstart;
double y = ystart;
for (int t=0; t<dx; t++)
{
setPixel(x,y);
x++;
y+=slope;
}
Der Bresenham Algorithmus ermittelt die Rasterpunkte ohne die Berechnung von Flie├čkommazahlen:
// Bresenham algorithm for 1. octant, 0<=slope<=1
// int xstart, ystart = start point of line segment
// int xend, yend = end point of line segment
// int dx = xend - xstart;
// int dy = yend - ystart;
// double slope = dy/dx;
// other octants similar
int x = xstart;
int y = ystart;
int err = 2*dy-dx;
for (int t=0; t<dx; t++)
{
setPixel(x,y);
x++;
if (err<0)
{
err += 2*dy;
}
else
{
y++;
err += 2*(dy-dx);
}
}
// int xstart, ystart = start point of line segment
// int xend, yend = end point of line segment
// int dx = xend - xstart;
// int dy = yend - ystart;
// double slope = dy/dx;
// other octants similar
int x = xstart;
int y = ystart;
int err = 2*dy-dx;
for (int t=0; t<dx; t++)
{
setPixel(x,y);
x++;
if (err<0)
{
err += 2*dy;
}
else
{
y++;
err += 2*(dy-dx);
}
}
← Baryzentrische Koordinaten Rechenbeispiel | ● | GL Antialiasing →